The NUS Guangzhou Research Translation and Innovation Institute is committed to building a platform for interdisciplinary and cross-domain scientific research exchange, promoting the effective transformation and application of research achievements. We will regularly share cutting-edge research results and updates in this section. We welcome your engagement and discussions!
This article introduces the research on high-performance P-channel CuI thin-film transistors based on HBr gas treatment conducted by Associate Professor Chunxiang Zhu’s team. His research focuses on semiconductor devices and their processing technologies. Chunxiang Zhu, ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR, is an IEEE Fellow and also serves as a Ph.D. supervisor at the NUS Guangzhou Research Translation and Innovation Institute (NUS GRTII).
Performance Enhancement of Solution-Processed CuI P-Channel Thin-Film Transistor by HBr Gas Treatment Method
Wei Wei, Ming Gao, Zhiyong Wang, and Chunxiang Zhu*
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, National University of Singapore
(*E-mail: elezhucx@nus.edu.sg)
High performance P-channel thin-film transistors (TFTs) with comparable device performance as N-channel metal oxide semiconductor TFTs are highly desirable to achieve Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (CMOS) circuits with low power dissipation. However, there are only a few P-channel candidates for P-channel TFTs, including CuxO, NiO, and CuI. Among different candidates, CuI has advantages of high hole mobility, low annealing temperature, and a wide bandgap (~3.1 eV). Solution-processed CuI TFTs with hole mobility larger than 1 cm2V-1s-1 have been developed. However, a high hole concentration in CuI makes the ON/OFF current ratio (ION/IOFF) at a low level of 101 ~ 102. In this work, HBr gas treatment method was proposed and adopted for the first time in treating the solution-processed CuI TFT to suppress the hole carrier concentration. The HBr treated CuI TFT shows an optimized device performance with a hole mobility of 3.0 cm2V-1s-1, an ION/IOFF ratio of 8.7×105, and good device stability.
1. TFT Device Fabrication and Material Characterization
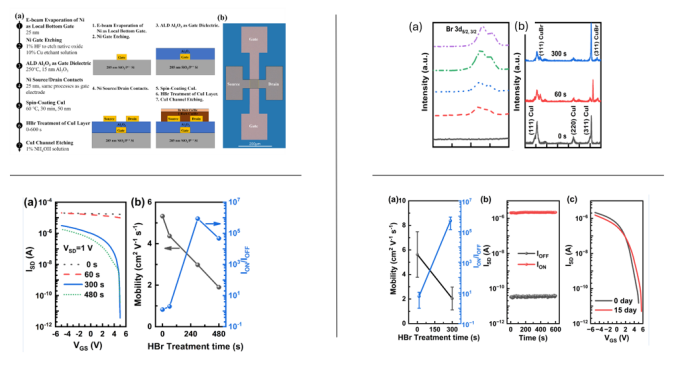
P-channel CuI TFT fabrication process flow is shown in top left figure. A 25 nm Ni layer was used as the bottom gate. ALD was used to deposit 15 nm Al2O3 as gate dielectric. Thereafter, source and drain metal electrodes were formed by e-beam evaporation of 25 nm Ni and the lift off process. The CuI active layer was fabricated by spin-coating CuI precursor solution and followed by an annealing. The samples with CuI TFTs were treated with HBr gas in the chamber of the RIE-ICP tool (Oxford Instruments). The total HBr treatment time varies from 0 to 600 s. Chemical states of CuI film surface with different HBr treatment time were studied using XPS. It is found that the Br/(I+Br) atomic ratio increases with HBr treatment time. XRD patterns for as-deposited and HBr treated CuI thin films with different HBr treatment time. The XRD results show that the as-deposited and HBr treated CuI thin films are polycrystalline.
2. P-channel CuI TFT Device Performance
The transfer curves of the CuI TFT as a function of HBr treatment time at VSD of 1V is shown in bottom left figure. The hole mobility and ION/IOFF ratio as a function of HBr treatment time were then extracted. Before the HBr treatment, the CuI TFT always operates at a normal ON state with a small ION/IOFF ratio of ~1.25. This is due to the high background hole concentration in pure CuI, which leads to the difficulty of tuning the CuI TFT to OFF state within the tested VGS range. With the increase of HBr treatment time from 0 s to 300 s, the OFF current decreases dramatically by a magnitude of 7 orders while at the same time the ON current of CuI TFT decreases marginally. This leads to the increase of ION/IOFF ratio to 8.7×105 with a HBr treatment time of 300 s. Meanwhile, the hole mobility of the device decreases slightly from ~5.3 cm2V-1s-1 to ~3.0 cm2V-1s-1. The I-V characteristics of the 300 s HBr treated CuI TFT devices were measured during cycling test and after 15 days. It was observed that the ON current and OFF current of the device were stable with an ION/IOFF ratio larger than 5×104 during this cycling test. All these results reveal the good stability of the HBr treated CuI TFTs.
Introduction of Project Leader

ZHU, Chunxiang
ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR
Dr. Zhu received his BEng degree in electronic material in 1992 and MEng degree in microelectronics in 1995, both from the Xidian University, Xi’an, China, and Ph.D degree in electrical and electronic engineering from the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Hong Kong, China in 2001.
He joined the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, National University of Singapore, Singapore, in February 2001 as an Assistant Professor. Since July 2007, he has been an Associate Professor. He has also been a Faculty Associate in Institute of Microelectronics (IME) since August, 2004. His research interests include semiconductor devices and processing. He is a member of IEEE.
The NUS Guangzhou Research Translation and Innovation Institute primarily focuses on seven key areas: smart city, information and communication, electronic science and technology, advanced manufacturing, artificial intelligence, biological sciences, and financial technology. Relying on NUS’ world-class research capabilities, the Institute has engaged dozens of professors from NUS as academic leaders. These leaders guide local research teams in promoting scientific research, research translation, and postdoctoral training programs.
We look forward to working with global research experts, entrepreneurs, and policymakers to stimulate innovative thinking, explore the infinite possibilities of scientific research, and establish an interdisciplinary and cross-field ecosystem for scientific research and innovative applications.


